Murata Noise Suppression Qi-Standard Power Supply Modules
In this study, Murata conducted noise assessments and examined noise suppression measures for both the wireless power supply transmitter and receiver modules compliant with the Qi standard. Murata also established methods for implementing effective noise suppression measures. Because measures are required by implementing remedies at both the receiver and transmitter sides, the measures implemented for each circuit type will be explained separately.Noise Issues in Wireless Power Supply Modules
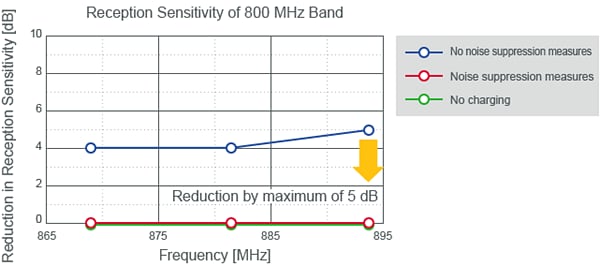
A study was conducted on whether the reception sensitivity for voice communication was reduced when supplying power wirelessly. It was determined the reception sensitivity was reduced in the 800MHz band when power was supplied wirelessly. A reduction in reception sensitivity also occurred uniformly in all frequencies.
Reception Sensitivity Measurement Results Diagram (800MHz band)

Noise Generation/Noise Propagation Mechanism
As a result of Murata's noise identification study, it proposed a mechanism by which noise is likely generated in the receiver module.
There are two main sources of noise.
• The first source is the charger.
• The second source is the receiver IC, which is located in the receiver module.
This noise is suspected to be emitted directly from the receiver module board or perhaps flowing through the power line or ground line and emitted from the smartphone board or wires. This noise creates a reduction in reception sensitivity when it flows to the antenna.
Circuit Diagram

Diagram of a simple equivalent circuit of wireless receiver module
Noise source: (1) Charger (flows to the receiver coil), (2) Receiver IC
Propagation mode: (1) Emitted from receiver module board, (2) Flows through power/ground line → Emitted from smartphone board or wires
There is noise emitted from the charger and noise occurring within the receiver module.
Note: The standard specifies the capacitors be installed in series with the transmitter coil of the charger and the capacitors be installed in series and in parallel with the receiver coil of the receiver module. The capacitors after the receiver IC are rectification capacitors. The wires in propagation mode (2) refer to the wires connecting the receiver module and smartphone and the wires in the smartphone.
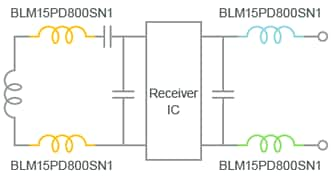
Noise Suppression Diagram

Diagram of noise suppression measures for wireless receiver modules diagram
Noise Suppression Measures
Murata then reviewed the simple equivalent circuit (noise suppression circuit) of the wireless receiver module.
Noise Suppression Circuit
Ferrite beads are installed at the base of the receiver coil (two locations) as shown in Figure 1 (below). As a result, noise that is emitted from the charger and flowing to the receiver coil is prevented from propagating within the receiver module.
Ferrite beads are installed in the power line and ground line connected to the smartphone. As a result, noise generated from the receiver IC is prevented from flowing to the smartphone.
Murata recommends the use of the BLM15PD800SN1 ferrite beads, which feature a compact size and support for large currents.
Figure 1

Simple equivalent circuit of a wireless receiver module (noise suppression measures)
The following noise suppression measures provide improved reception sensitivity for voice communication.
(1) Ferrite beads at the base of receiver coil (Murata recommends BLM15PD800SN1)
(2) A ferrite bead on the power line connected to the smartphone (Murata recommends BLM15PD800SN1)
(3) A ferrite bead on the ground line connected to the smartphone (Murata recommends BLM15PD800SN1)
Measure (1) is effective for noise that is emitted from the charger and that flows to the receiver coil.
Measures (2) and (3) are effective for noise generated in the receiver IC.
Note: If the flux leakage from the charger is large, noise suppression measures for the receiver side only may not improve the reception sensitivity. Noise suppression measures must also be fully implemented at the charger. Also, if the flux leakage from the charger is large, noise that is emitted from the transmitter coil will flow directly to the antenna. Therefore, measures that use ferrite beads will not be effective. In this case, the electromagnetic wave absorbing sheet can be enlarged beyond the receiving coil (as if affixing to the entire case) to keep noise from flowing to the antenna and to improve the reception sensitivity.
Effect on Resonance Frequency of Circuit
Murata studied whether the noise suppression measures in the above figure have an adverse effect on charger operation.
This is an issue because, if the impedance characteristics formed by the circuit (receiver coil + series capacitor, receiver coil + series capacitor + parallel capacitor) are changed when ferrite beads are installed, the power transmission and reception also change.
In the Qi standard, it is specified:
Resonance frequency for the receiver coil + series capacitor = 100kHz +5% -10%
Resonance frequency for the receiver coil + series capacitor + parallel capacitor = 1000kHz ±10%
Murata calculated how the impedance characteristics of the circuit (receiver coil + series capacitor in this example) change when ferrite beads were installed. This was calculated assuming the inductance value and capacitance value were two different types.
Calculation of Impedance Diagram
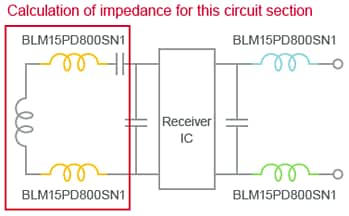
Condition (1): Transmitter coil = 25uH、Series C = 100nF
Condition (2): Transmitter coil = 10uH、Series C = 250nF
Condition (1) is the actual-measured value that was set to the system provided for evaluation, and Condition (2) was set so that the inductance drops to less than half of the above value. (This is because the effect of ferrite beads becomes more pronounced as the inductance of the transmitter coil becomes smaller.)
Conditions

Murata determined installing the ferrite beads had no effect on the impedance characteristics of the circuit. Therefore, Murata thinks even if ferrite beads are installed, their effect on charger operation is small.
Note: Compared to the inductance value (about 10uH to 20uH) of the receiver coil, the L value of the BLM15PD800SN1 is a small value of only 210nH (actual value measured by LCR meter), and so the resonance frequency can be said to remain unchanged.
Effect of Noise Suppression Measures
Murata evaluated the reception sensitivity when power is supplied wirelessly while the noise suppression measures described in the previous section were implemented.
As a result, the reception sensitivity improved for all frequencies. In this sample evaluation, the reception sensitivity improved by up to 5dB, and the drop in reception sensitivity when power was supplied wirelessly was zero.
Reception Sensitivity for Voice Communication Diagram
Simple Equivalent Circuit of a Receiver Module Diagram
Noise suppression measures using ferrite beads enable a significant improvement in reception sensitivity.
Summary of Noise Suppression Measures for Receiver Modules
Noise Issues for Wireless Receiver Modules
Noise generated by the charger flows from the transmitter coil to the receiver coil, and the insertion of a wireless circuit lowers the reception sensitivity of the wireless circuit.
Noise Suppression Measures
As shown below, ferrite beads are used at the receiver circuit to implement noise suppression measures and improve the reception sensitivity of the wireless circuit.
(1) Installation of ferrite beads at the base of the receiver coil (Murata recommends BLM15PD800SN1)
(2) Installation of a ferrite bead on the power line connected to the smartphone (Murata recommends BLM15PD800SN1)
(3) Installation of a ferrite bead on the ground line connected to the smartphone (Murata recommends BLM15PD800SN1)
Wireless Transmitter Modules Diagram

Noise Suppression Measures for Wireless Transmitter Modules
Following the receiver module, Murata examined the noise that must be suppressed in the transmitter module. In the transmitter module, the inverter used for supplying AC to the transmitter coil is a noise source. The noise emitted from the power supply cable becomes an issue as externally emitted noise, and noise that flows into the transmitter coil side is emitted externally, reducing the reception sensitivity of the smartphone unit.
Consequently, Murata recommends noise suppression measures for preventing noise emissions and for preventing drops in reception sensitivity.
Noise issue locations

Emission noise: (1) Transmitter coil and (2) Power supply cable
Reception sensitivity: (1) Transmitter coil
First, Murata implemented the measures for preventing emission noise. This consists of noise that leaks to the power supply cable side from the inverter and noise that leaks to the transmitter side. Noise suppression circuits are installed for each location. (Suppression measures (1) and (2))
Because emission noise consists primarily of noise transmitted in common mode, a common mode choke coil is used. A line bypass capacitor is also used because the transmitter coil side contains a large amount of high-frequency noise.
Next, Murata implemented measures for preventing drops in reception sensitivity. The noise suppression measures were implemented in the same way as those at the transmitter coil side for preventing emission noise. A common mode choke coil and line bypass capacitor were used. As a result, reception sensitivity was improved by up to 12dB.
Preventing drops in the reception sensitivity

Summary
To summarize noise suppression measures for transmitter modules:
• The inverter of the transmitter module is a source of noise, and noise flows to and is emitted to the power supply cable side and transmitter coil side, resulting in emission noise and a reduction in reception sensitivity.
• Filters combining a common mode choke coil and capacitor were installed at the inverter power supply cable side and transmitter coil side for suppressing emission noise and preventing drops in reception sensitivity.
Transmitter Module Diagram

Community Forum
Murata Community Forum provides searchable content with various discussion topics, popular blogs, and articles. The Murata broad market support team holds regular reviews to discuss open issues, allowing inquiries to be answered in a timely manner. The forum content is freely accessible to the public. However, users must log in to post questions or answers. Registration is free of charge.